Introduction
A paint gloss meter is a specialized instrument designed for measuring the gloss level of surfaces, primarily those coated with paint. Gloss, a key attribute in the quality control of surface coatings, refers to the ability of a surface to reflect light in a specular (mirror-like) direction. The gloss level of a surface can significantly affect its appearance and performance, making gloss measurement a critical aspect in various industries, including coatings for automotive, furniture, consumer and industrial goods manufacturing.
Fundamentals of Paint Gloss Measurement
The principle of gloss measurement hinges on the physical property of light reflection. When light strikes a surface, it gets reflected in various directions. A surface with high gloss reflects light in a more uniform and specular manner, whereas a low-gloss surface scatters light more diffusely. Paint gloss meters quantify this phenomenon by directing a light beam at a fixed intensity and angle onto the surface and measuring the amount of light reflected.
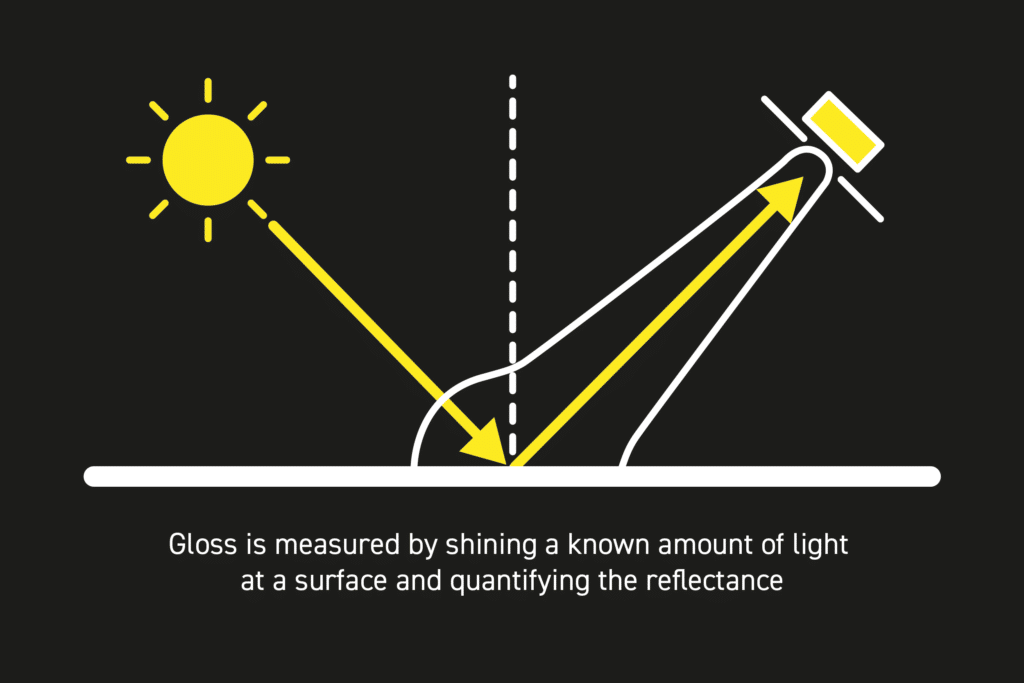
Gloss is quantified in gloss units (GU), a scale determined by comparing the surface in question to a standard (usually a polished black glass reference) with a defined gloss value. Most paint gloss meters use angles of 20°, 60°, or 85° for measurement, with each angle catering to different levels of surface gloss:
- The 20° angle is ideal for high-gloss surfaces, where gloss levels are above 70 GU
- The 60° angle is the most versatile, suitable for medium gloss surfaces (10-70 GU) and most commonly used in the automotive paint industry
- The 85° angle is used for low-gloss surfaces, typically below 10 GU.
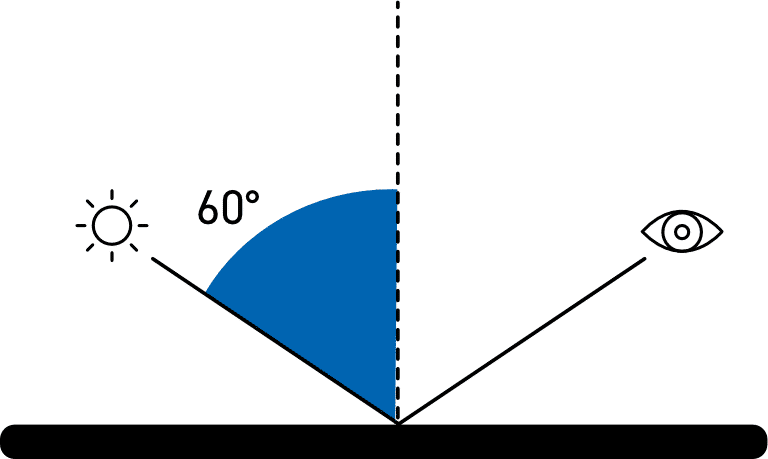
Universal Measurement Angle: 60°
All gloss levels can be measured using the standard measurement angle of 60°. This is used as the reference angle with the complimentary angles of 85° and 20° often used for low and high gloss levels respectively.
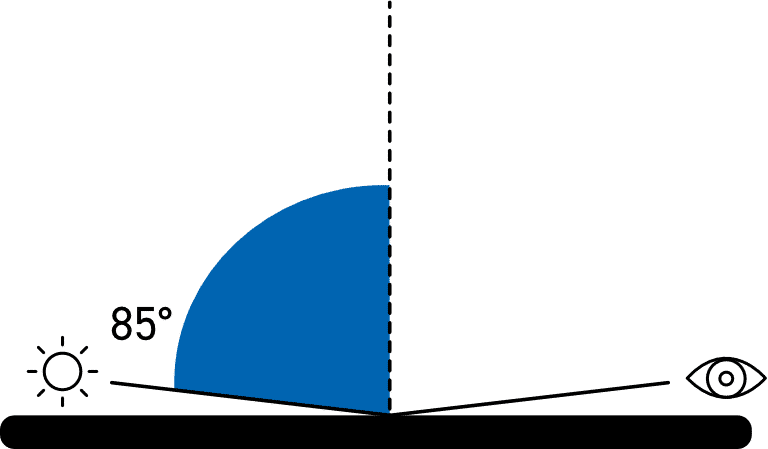
Low Gloss: 85°
For improved resolution of low gloss a grazing angle of 85° is used to measure the surface. This angle is recommended for surfaces which measure less than 10GU when measured at 60°.
This angle also has a larger measurement spot which will average out differences in the gloss of textured or slightly uneven surfaces.
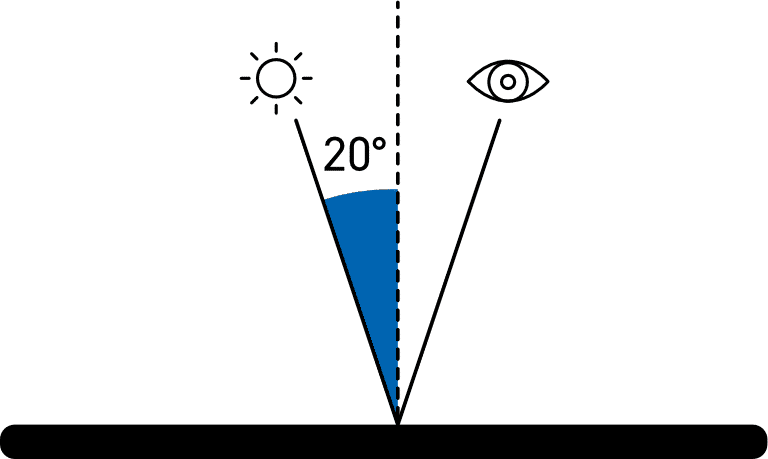
High Gloss: 20°
The acute measurement angle of 20° gives improved resolution for high gloss surfaces. Surfaces that measure 70GU and above at the standard angle of 60° are often measured with this geometry.
The 20° angle is more sensitive to haze effects that affect the appearance of a surface.
Application of Paint Gloss Meters
In practical terms, paint gloss meters find extensive application in quality control processes. Manufacturers use these instruments to ensure consistency in production, particularly in sectors where aesthetic appeal is paramount. For example, in the automotive industry, a uniform gloss level across different car parts is crucial for visual appeal. Similarly, in the furniture industry, the gloss of varnishes and lacquers can significantly impact the product’s market appeal.

International Standards for Gloss Measurement
Gloss measurement is governed by several international standards to ensure consistency and reliability. The most widely recognized standards include:
- ASTM D523: The Standard Test Method for Specular Gloss, established by the American Society for Testing and Materials. This standard defines the method for measuring the gloss of non-metallic surfaces using a gloss meter
- ISO 2813: Published by the International Organization for Standardization, this standard specifies methods for measuring the gloss of paint and varnish coatings
- DIN 67530: The Deutsches Institut für Normung standard, which aligns closely with ISO 2813, also defines the measurement of gloss levels on flat surfaces.
Adherence to these standards ensures that gloss measurements are consistent and comparable across different industries and geographical locations.
Calibration of Paint Gloss Meters
Calibration of paint gloss meters plays a critical role in ensuring accurate and reliable measurements
Calibration involves the adjustment of the gloss meter to a known standard, typically a calibration tile provided by the manufacturer, with a known gloss value.
Importance of Gloss Meter Calibration
The accuracy of gloss measurements is highly dependent on the instrument’s calibration. Over time, the performance of gloss meters can drift due to factors like aging of electronic components, changes in environmental conditions, and wear and tear. Regular calibration corrects these deviations, ensuring that the measurements remain true to the actual gloss levels of the surfaces being tested.
UKAS / ISO 17025 accredited laboratories provide traceability to recognized international standards, ensuring that measurements are aligned with global benchmarks.
Customers benefit from confidence in the accuracy and consistency of their measurement equipment, reducing the risk of errors and inaccuracies.
Quality Assurance
- UKAS accreditation signifies a commitment to quality and competence in calibration services
- Customers receive assurance that their instruments are calibrated by skilled professionals using state-of-the-art equipment, resulting in reliable measurements.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
- Many industries and regulatory bodies require equipment calibration to be performed by accredited labs
- Using a UKAS accredited laboratory helps customers meet these compliance requirements, avoiding potential legal issues and fines.
Consistency and Reliability
- Calibration performed by UKAS accredited labs follows rigorous and standardized procedures
- Customers benefit from consistent, repeatable, and reliable measurements, which are crucial in critical applications and industries like healthcare and aerospace.
Reduced Risk of Errors
- Calibration errors can lead to costly mistakes or product defects
- Customers gain peace of mind knowing that their instruments are calibrated with the utmost precision, minimizing the risk of errors in their processes or products.
Enhanced Productivity
- Accurate measurements lead to improved efficiency and productivity
- Customers can optimize their operations and reduce wastage, ultimately saving time and resources.
Data Integrity and Documentation
- UKAS accredited labs provide detailed calibration reports and documentation
- Customers benefit from comprehensive records that can be used for auditing, compliance, and quality control purposes.
Competitive Advantage
- Demonstrating the use of UKAS accredited calibration services can enhance a company’s reputation and credibility
- Customers can leverage this advantage when seeking new clients or partnerships, as it reflects a commitment to quality.
Cost Savings
- Accurate calibration helps extend the lifespan of equipment and prevents premature replacement
- Customers can save money by avoiding unnecessary equipment repairs or replacements due to calibration-related issues.
Global Acceptance
- UKAS accreditation is internationally recognized and respected
- Customers can confidently use equipment calibrated by UKAS accredited labs in various global markets without concerns about measurement inconsistencies.
Customer Confidence
- When customers know that a business relies on UKAS-accredited calibration, they have greater confidence in the products and services they receive
- This can lead to increased customer loyalty and repeat business.
An equivalent to UKAS certification in Europe is an ENAC laboratory.
Examples of gloss meter calibration laboratories offering these services include:
- Rhopoint Instruments, gloss meter manufacturer
- Neurtek Instruments, worldwide gloss meter service and support
Frequency of Calibration
The frequency of calibration depends on factors like the frequency of use, the operating environment, and the manufacturer’s recommendations. Typically, calibration is recommended at least once a year or after any repair or servicing of the instrument.
Conclusion
Paint gloss meters are indispensable tools in the realm of surface coating quality control, offering precise quantification of gloss levels. Adherence to international standards ensures uniformity and comparability of gloss measurements, enhancing their reliability. The calibration of these instruments is a non-negotiable aspect of their operation, pivotal for maintaining measurement accuracy and thereby upholding the quality standards in various industries. As such, understanding the principles, usage, and calibration of paint gloss meters is essential for professionals engaged in the manufacturing and quality control of surface coatings.